What is a Heat Exchanger?
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two or more fluids without mixing them. Typical forms include shell & tube, plate heat exchangers, spiral, block type heat exchangers, plate coils and air-cooled units. These products are used across food, chemical, pharma, power, oil & gas, HVAC, & various other industrial sectors.
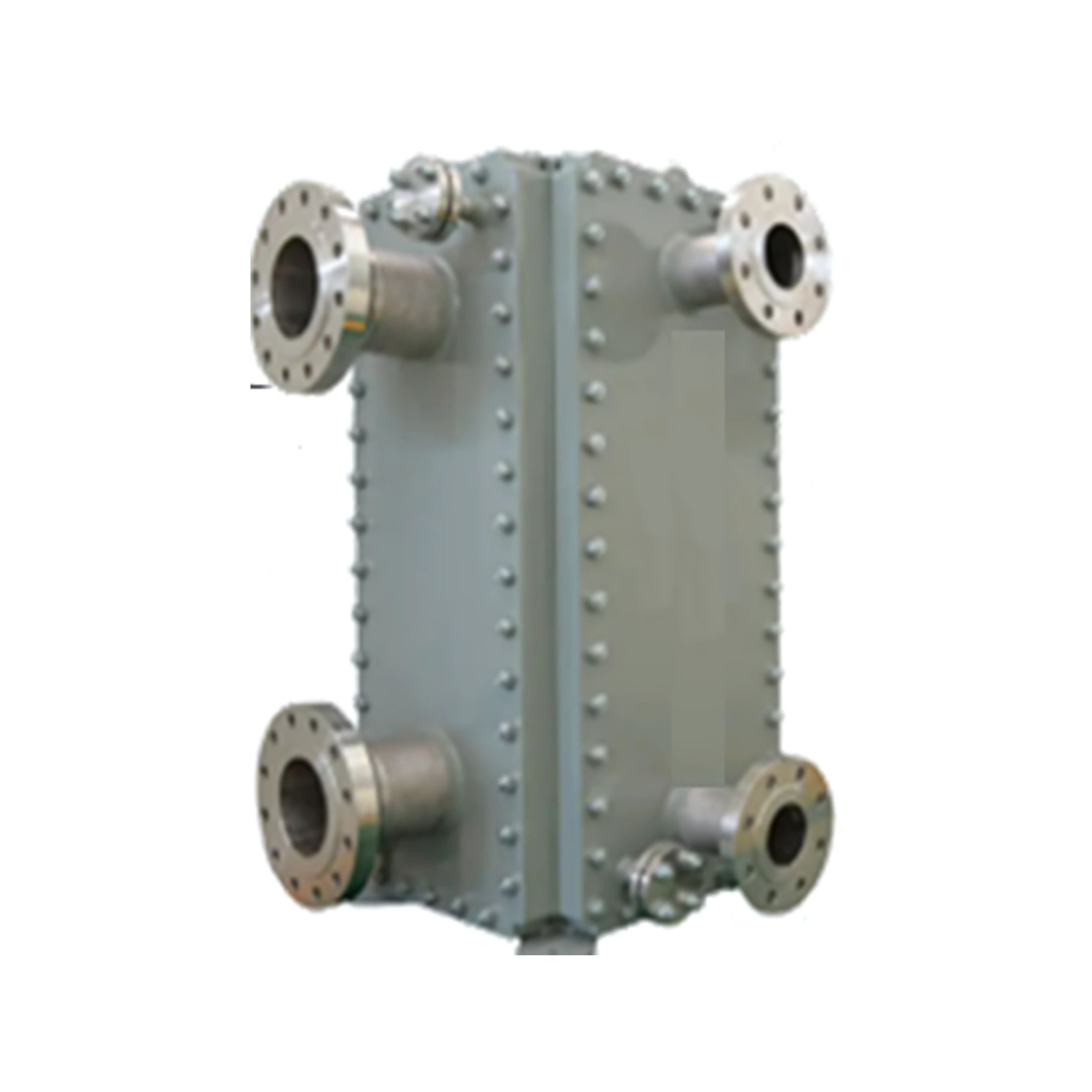

Block Type Heat Exchangers
A block type heat exchanger is a customized heat transfer unit where tubes, plates, or coils are enclosed within a rectangular or square block-shaped casing. The design provides flexibility to handle multiple fluid streams, large flow volumes, and non-standard layouts, making it suitable for specialized process requirements.
Key Benefits Include:
- Design flexibility to accommodate unique process conditions
- Compact and robust construction for efficient use of space
- High versatility with options for air, liquid, or gas cooling/heating
- Ease of integration with existing process systems and ducts
Applications
Block type heat exchangers are used in HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, power plants, food & beverage processing, and other industries where tailored solutions are required for air or process fluid heat recovery.
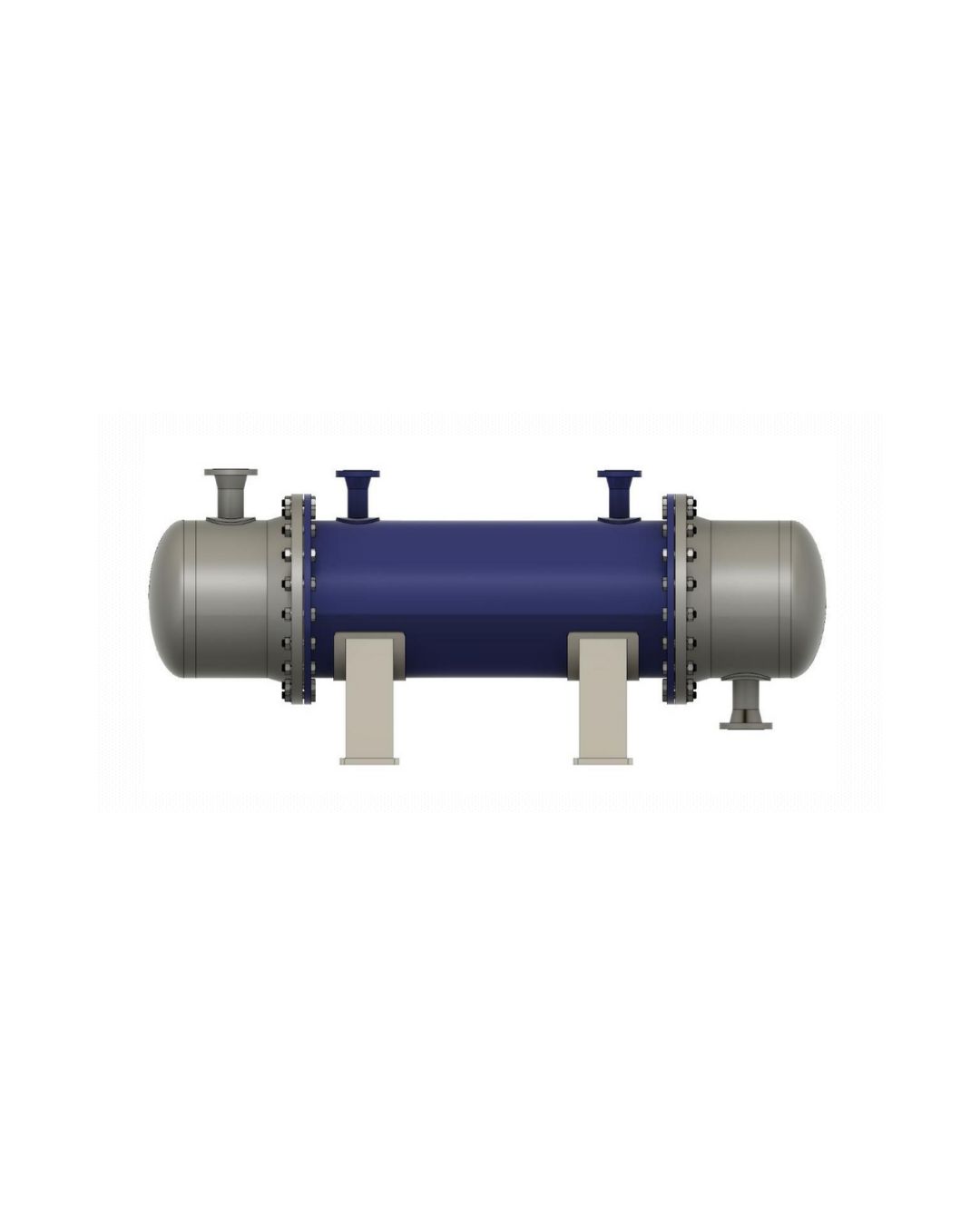
Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers
The shell & tube heat exchanger is the most widely used and time-tested heat exchanger design. It consists of a bundle of tubes enclosed within a cylindrical shell, with one fluid flowing inside the tubes and another fluid around them. The robust construction makes it suitable for a wide range of pressures, temperatures, and applications.
Key Benefits Include:
- High durability and reliability for continuous, heavy-duty operations
- Versatile design adaptable to condensation, evaporation, and heat recovery duties
- Handles extreme conditions with high pressure and temperature capabilities
- Ease of cleaning and maintenance through removable tube bundles
Applications
Shell & tube heat exchangers are extensively used in oil & gas, power generation, chemical, petrochemical, marine, and process industries, making them a standard choice where performance and longevity are essential.

Plate Heat Exchangers (PHE)
A plate heat exchanger consists of multiple thin, corrugated plates stacked together to create separate flow channels for hot and cold fluids. The large surface area and turbulent flow patterns deliver highly efficient heat transfer in a compact unit.
Key Benefits Include:
- Excellent thermal efficiency due to large surface area and counter-current flow
- Compact and space-saving compared to shell-and-tube exchangers
- Flexible capacity -- easy to add or remove plates as process demands change
- Cost-effective with lower material usage for the same duty
Applications
Plate heat exchangers are widely used in HVAC, refrigeration, dairy, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemical, and power industries where high efficiency, hygiene, and easy maintenance are critical.
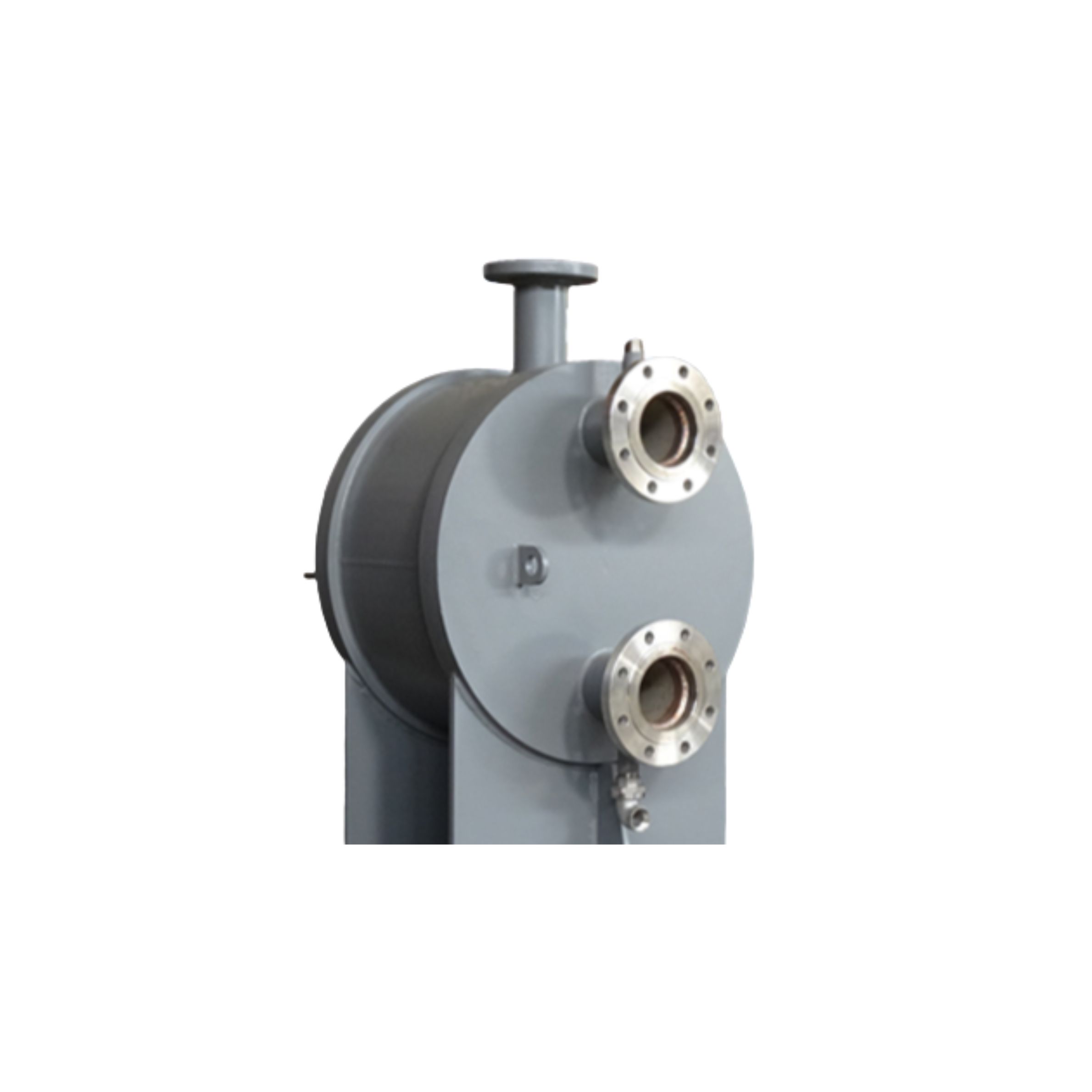

Shell & Plate Heat Exchanger
A shell & plate heat exchanger combines the robustness of a shell-and-tube design with the efficiency of plate technology. It consists of a fully welded plate pack inserted into a cylindrical shell, creating a compact, leak-tight unit capable of handling high pressures and temperatures.
Key Benefits Include:
- High thermal efficiency with true counter-current flow
- Compact design with a smaller footprint than traditional shell-and-tube exchangers
- High pressure and temperature resistance due to fully welded construction
- Low maintenance with no gaskets, ensuring reliability in demanding conditions
Applications
Shell & plate heat exchangers are commonly used in oil & gas, power generation, chemical processing, and refrigeration industries, particularly where efficiency, durability, and space savings are critical.
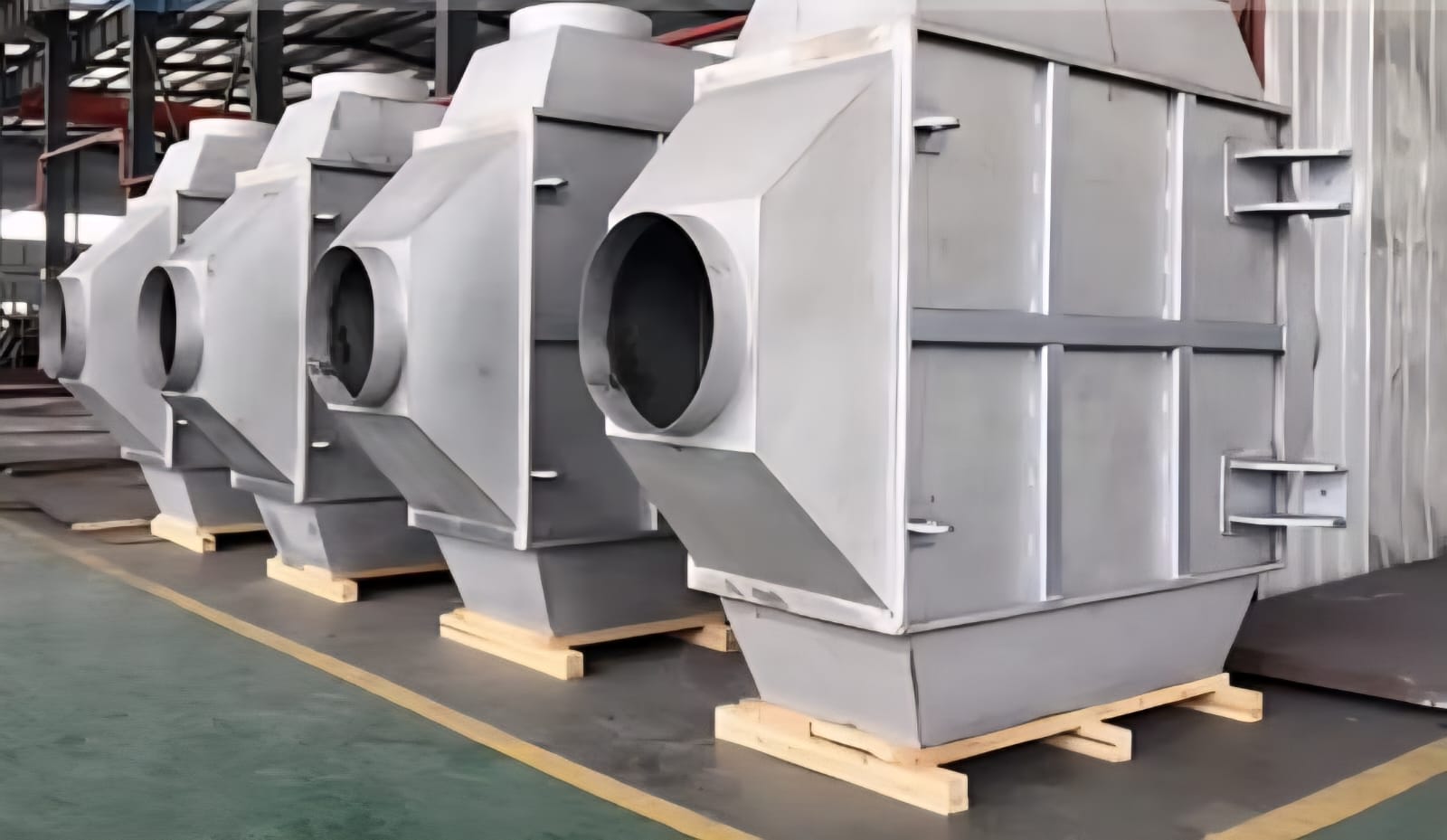

Energy Recovery Economisers
Grevia provides modular, flexible, and economical economiser solutions that serve as waste heat recovery systems. These heat exchangers transfer waste heat from exhaust gas streams to incoming air or water, significantly improving system efficiency.
Key Benefits Include:
- Modular design for flexible installation options
- Available in carbon steel and stainless steel materials
- Various tube types to match specific process parameters
- Multi-stage dry/wet systems capability
- Customizable configurations for diverse applications
- Efficient heat transfer technology
- Robust construction for long-term reliability
Environment & Climate Benefits
With rising energy costs and CO₂ emission restrictions, our economisers help facilities utilize energy more efficiently by capturing waste heat from various process areas. This approach reduces fuel consumption and increases overall plant productivity.
Offered Services
ASME Code
- Quality Control Manual
- Design Calculations as per ASME Sec VIII Div-1 U Stamp
- Drawings as per requirements of Code
- Material specifications as per Code
- Name plate drawings
- Complete Dosier
Static Equipment Packages
- 3D Modeling
- Skid Structure
- Equipment Layout
- Detail Drawings of Skids
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Piping Isometric Drawings
- PDMS Modeling
Mechanical & Thermal Design
FEA & Stress Analysis
- Primary Local Membrane Stress
- Bending Stress
- Secondary Membrane Stress
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Validation of conceptual thought & Processes in Industry
- Performance & Rating of Heat Exchangers
Value Engineering
- Reverse Engineering
- Process Validation
- Software for Heat Transfer